Activated carbon is pyrolyzed organic matter that undergoes thermal and/or chemical activation to increase the porosity and surface area. These internal pores are what captures impurities in air or water filtration.
Thermal activation occurs with steam or carbon dioxide at extremely high temperatures. Chemical activation occurs when the carbon is exposed to a dilute acid at elevated temperatures.
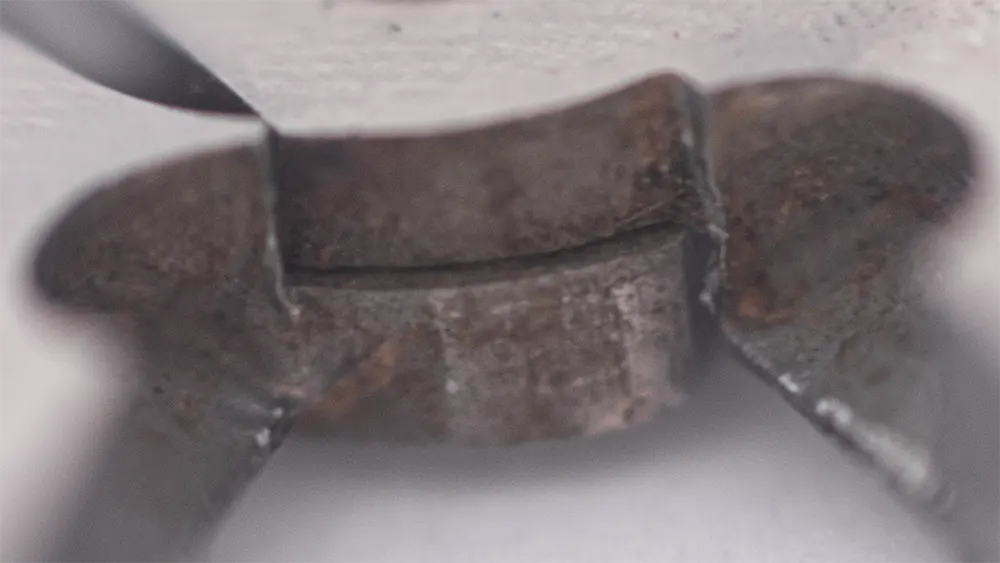
Corrosion occurs when air filtered through acid-washed carbon is recirculated in an enclosure. This can be minimized or prevented by using acid-free activated carbon. Also, using corrosion resistant materials, such as stainless steel or aluminum, will increase protection.
Acid Washed Carbon Damaging 3D Printers
A novel problem with acid-washed carbon has emerged in the additive manufacturing industry. It involves FDM and Resin printers utilizing activated carbon to mitigate VOCs from off gassing plastic and photopolymer.
When these printers are enclosed and recirculate the air through the carbon, leftover acid compounds are dislodged. These acidic chemicals build up in concentration within the enclosure, resulting in corrosion on metal components.
Why Is Most Activated Carbon Acid Washed?
Most activated carbon available online is washed with acid to increase its effectiveness and purity. It will reduce the ash content as well.
The use of both thermal and chemical activation can provide a greater porosity and surface area than just one method alone. Increasing these will improve the efficiency and holding capacity of the carbon.
Activated carbon used for water filtration needs to be pure to ensure safety for drinking water or aquariums. Acid washing the carbon can remove impurities on the surface of and within the granules. Iron, silicon, potassium, and aluminum are some of the elemental impurities.
Acid washing activated carbon will reduce the ash content, which is particularly desirable for air filtration. However, using activated carbon derived from coconut shells is the easiest way to minimize ash.
Ash Content Approximations:
- Acid-Washed Coconut Shell Carbon: <3-5%
- Acid-Free Coconut Shell Carbon: <5%
- Coal-Based Activated Carbon: 8-15%
Using Acid Free Activated Carbon
To avoid the risk of corrosion, you will want to use acid free activated carbon. You can buy our acid free carbon or test various brands.
Our supplier claims that the carbon is acid free, but to ensure quality, we continue random testing.
4D Filtration carbon is tested for acidity by two methods:
- High airflow for 48 hours at room temperature
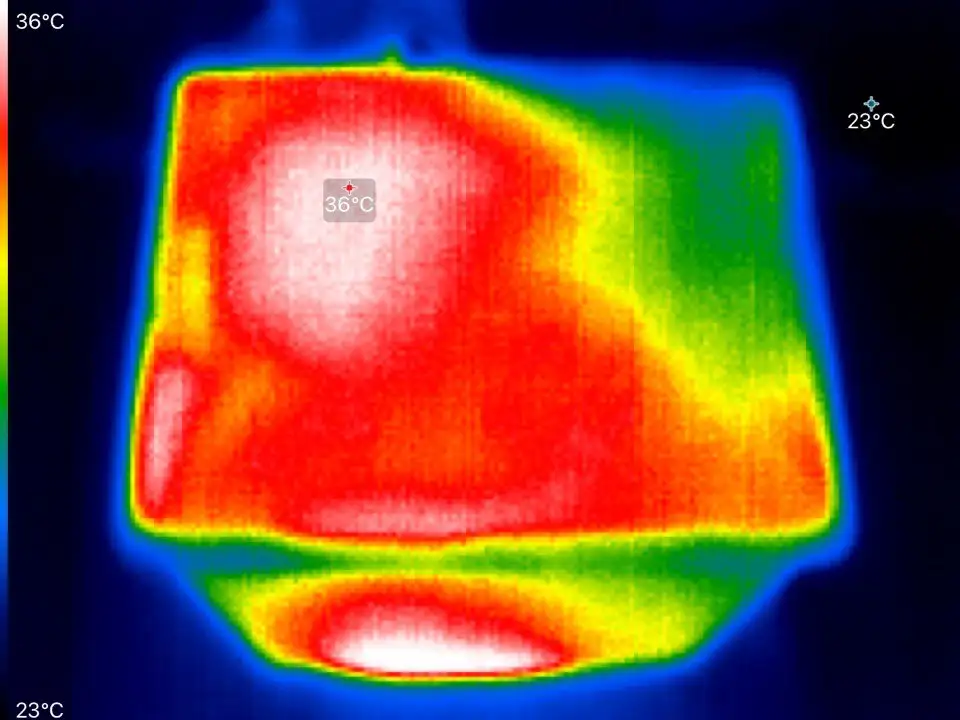
- High airflow for 6 hours at 35-40°C
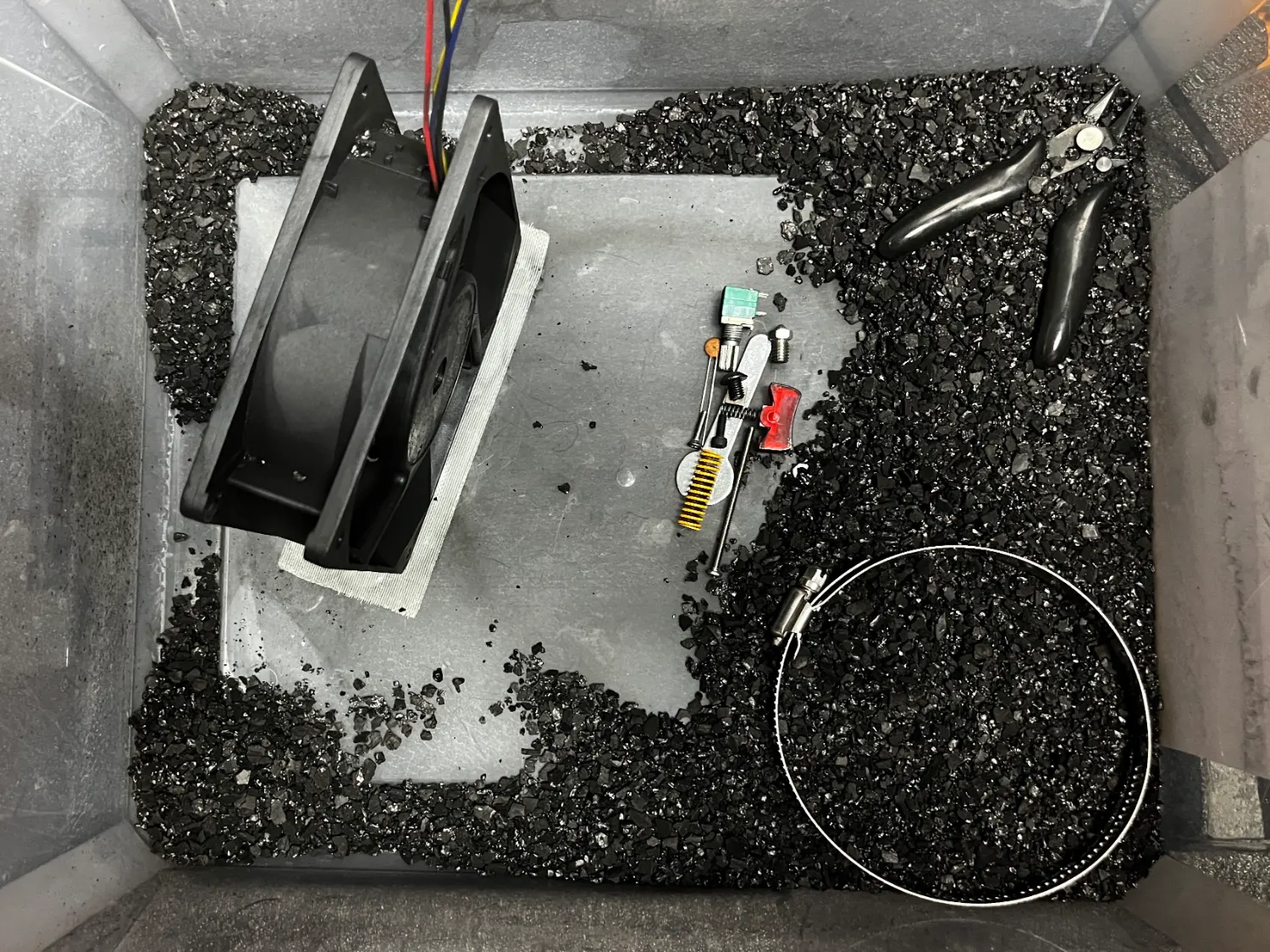
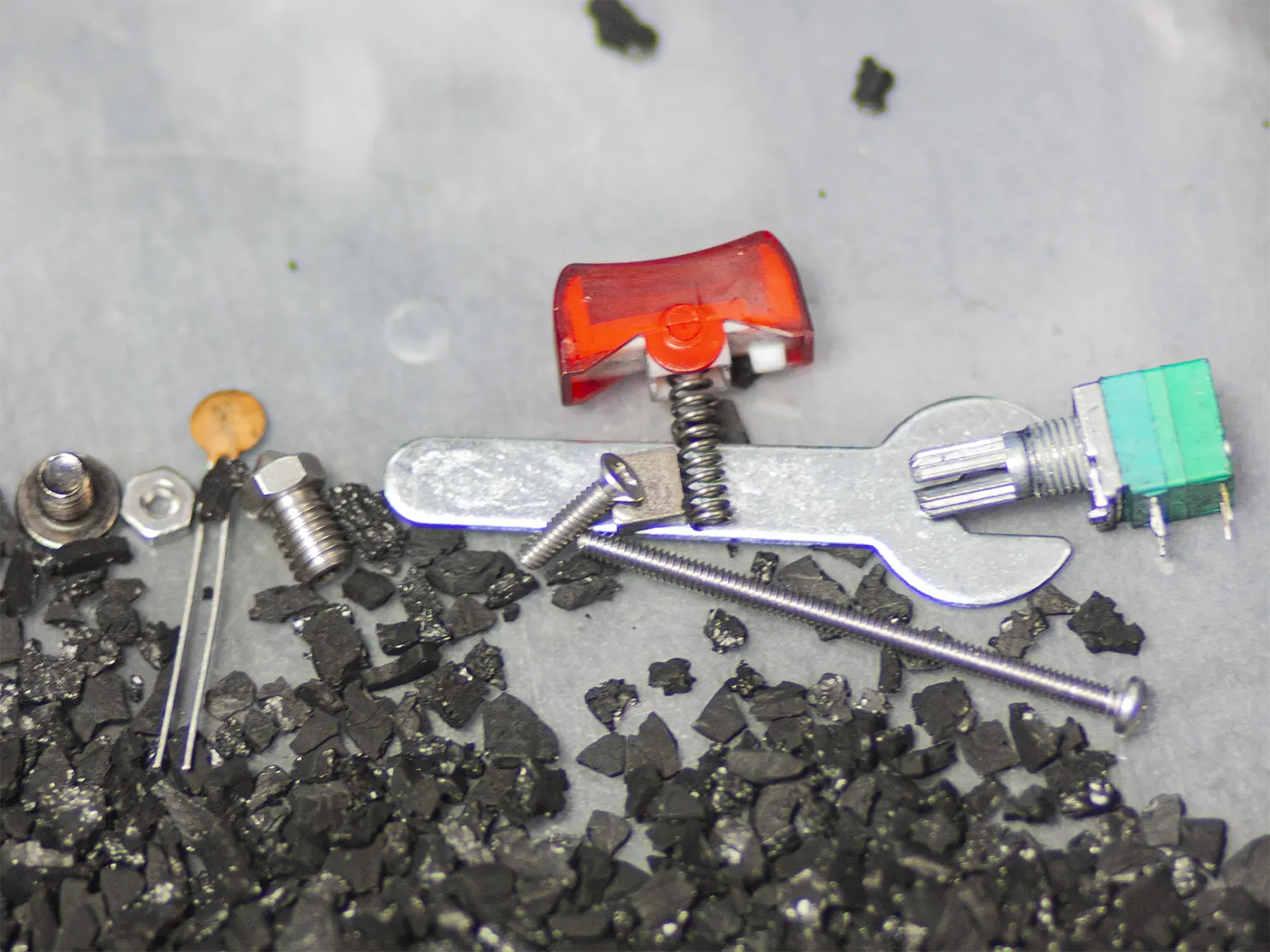
Our test setup uses one of our 178 CFM fans in a container with at least 300 grams of loose carbon granules. The 120 mm fan is secured to the container using double-sided tape. The violent combination of loose granules with the powerful fan will occasionally shred granules into a powder, which arguably assists in the test. The heated test uses a small ceramic heater with a temperature controller.
We will continue random testing to ensure that our activated carbon is acid free.
Disclaimer: You assume all responsibility and risk for the use of, but not limited to, the resources, advice, and opinions of 4D Filtration or its employees. 4D Filtration or its employees do not assume any liability or create any warranty for the use of any information. 4D Filtration may receive commissions for referral links. Prices are approximated for simplicity and they may fluctuate due to sales or markdowns. Amazon .com should refer you to your local amazon site if you are not in the United States; there is a chance Amazon's link redirect system will take you to a different product.